Sure, if you’re to take customer success at face value, it sounds relatively simple. “Customer” plus “success” equates to the eventual success of a customer with the product or service they’ve purchased.
While its ethos is uncomplicated, there are a lot of nuanced moving parts that need to be understood before your customers reach their goals. In fact, we’d call these the fundamental elements of customer success.
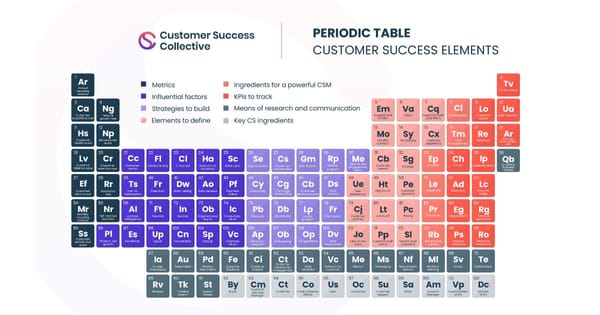
We’ve created our very own periodic table of what elements are indispensable to customer success. There are a lot of factors, traits and metrics responsible for making customer success, as a business function, work, but mastering them is your one-way ticket to being the best Customer Success Manager for your clients, your business, and your career.
Why have we created a customer success periodic table?
The periodic table organizes chemical elements into groups allowing scientists to easily determine the properties of individual elements. We all recognize the periodic table. But it’s not just an iconic image, the periodic table groups elements together and explains how they relate to one another.
Our customer success periodic table contains every fundamental component needed to help your customers be successful. You can use this as a visual framework, whether that’s saved as your desktop background, or shared amongst your team, to help decipher the various elements that make up a knock-out customer success strategy.
Because we’re such suckers for details, we’ve created our customer success periodic table in the same vein as the (scientific) periodic table.
Each part is divided into sections, with each section representing a different category. These are:
- Metrics
- Influential factors
- Strategies to build
- Elements to define
- Ingredients for a powerful CSM
- KPIs to track
- Means of research and communication
- Key customer success ingredients
Let’s take an in-depth look at what we’ve put in each category. 👇
Metrics
There’s no point in any business function if you can’t measure the success or failures of an endeavor.
Being able to gauge how well a new initiative has been received, or simply receiving feedback, is of invaluable importance to any professional. Any credible, revenue-generating customer success department knows one crucial thing: being analytical and backing up your efforts with data gathered by metrics is a shoo-in to get the support of your leadership team.
Here are just some of the 13 key customer success metrics we identified as being the beating heart of any CS function. These are:
Ar 1: Annual recurring revenue
The amount of predictable annual revenue expected from existing customer contracts.
Ca 3: Customer-acquisition cost
The total cost involved with acquiring each new customer.
Ng 4: Natural growth rate
The organic expansion of revenue attributed to existing customers increasing their usage, or adding licenses without the intervention of a sales team.
Hs 11: Customer health score
A broad metric that gauges the overall status of a customer relationship based on several factors like usage, engagement, and satisfaction.
Np 12: Net promoter score
A metric that measures customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend a company's products or services to others.
Lv 19: Customer lifetime value
The total revenue expected from a customer during the entire lifespan of their relationship with a business.
Cr 20: Customer retention cost
The total cost involved with activities aimed at retaining existing customers.
Ef 37: Customer effort score
A measure of how easy or difficult it is for customers to interact with a company and get support.
Rr 38: Resolution rate
The percentage of customer cases, issues, or support tickets that are resolved to their satisfaction.
Mr 58: Monthly recurring revenue
Revenue that a business can expect on a monthly basis from existing customer contracts.
Nr 55: Net revenue retention
The measure of expansion or contraction from existing customers over a period of time.
Ss 85: Customer satisfaction score
A quantitative metric gauging how happy or satisfied customers are with a product, service, or experience.

Influential factors
Influential factors are the real driving forces behind a successful customer success strategy. They encompass the broader environment in which customer success operates, including market trends, customer expectations, and technological advancements.
Understanding these factors enables Customer Success Managers (CSMs) to better tailor their strategies to the current landscape.
Here are 17 influential factors we identified:
Cc 21: Customer-centric
A strategy that focuses on customer needs, experience, and satisfaction at the core of company priorities and operations.
Fl 22: Feedback loop
An ongoing process to regularly collect, analyze, and act on customer feedback.
Cs 23: Cross-sell
Selling complementary products or services to existing customers.
Ha 24: Sales-to-CS handover
The transitioning of customer relationships from the sales team to customer success after closing a deal.
Sc 25: Sales cycle
The length of time that passes from initial contact with a customer to closing a sale.
Ts 39: Trial-to-subscription
The process of converting customers from free trial status to paid subscribers of a software or service.
Fr 40: Freemium
A pricing model that offers a free version of a paid-for product to customers.
Dw 41: Down-selling
Transitioning customers to smaller, less expensive package offerings that better fit their current needs.
Ao 42: Autorenewal
The automatic renewal of a subscription at the end of a contract term unless the customer cancels.
Pf 43: Payment failure
Instances where a customer payment does not go through successfully due to expired cards, incorrect billing details, insufficient funds, etc.
Ai 56: Artificial intelligence
Software or machines that can perceive environments, solve problems, and complete tasks to achieve goals with human-like capabilities.
Ft 71: Free trial
Giving customers full access to try a product for free for a limited time before requiring payment.
In 72: Inactive
Customers who have low or no engagement with a product or service in a given period.
Ob 73: Organizational buy-in
Getting agreement and support from stakeholders across a company to back initiatives and strategies.
Ic 74: Involuntary churn
Customer turnover that occurs due to factors outside of the customer's direct control, such as failed payments and service cancellations.
Pl 86: Product-led growth
A business strategy focused on leveraging the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, retention, and expansion.
Es 87: Escalation
The handing off of a customer issue to a higher tier of support when initial contacts could not resolve the case.
Up 88: Upsell
Successfully convincing customers to upgrade to more expensive products or service tiers.
Cn 103: Cancellation
The ending of a customer contract or subscription before the end of the current term.
Sp 104: Startup
A fledgling business in the early stages of operations working to find product/market fit.
Vc 105: Voluntary churn
Customer turnover initiated directly by the customer rather than the vendor.

Strategies to build
This section focuses on actionable strategies to directly improve customer success. This involves putting plans into motion and striving for tangible results.
Implementing these strategies can lead to better customer acquisition, expansion, retention, and engagement.
Key elements in this category include:
Se 36: Segmentation
Dividing customers into groups that share common attributes, behaviors, or needs to target strategies more precisely.
Cs 27: Customer success plan
An outline of goals, metrics, and actions designed to ensure and expand the value customers gain from a product or service.
Gm 28: Gamification
Using game mechanics like scoring, levels, challenges, etc. to drive user engagement with products.
Rp 29: Referral program
An initiative that rewards existing customers for referring new users in order to drive growth through advocacy.
Me 30: Mutual-led engagement plans
Strategies and timelines to ensure continued customer interactions and value delivery developed mutually between client and provider.
Cy 44: Case study
A detailed analysis showcasing how a customer achieved success or overcame challenges through working with a product or service.
Cg 45: Concierge onboarding
Using a high-touch approach, this white-glove onboarding experience with extensive hand-holding and account configuration
Cb 46: Customer advisory boards
A select group of customers that provide ongoing advice and feedback to help shape a company's product and service direction.
Ds 47: Data science
Leveraging statistical, computational, and scientific processes to derive insights from data sources.
Pb 75: Playbook
A set of defined processes, guidelines, training, and assets that combine to provide set ways for teams to successfully perform key tasks.
Db 76: Dashboard
A data visualization tool that displays critical metrics, KPIs, and insights in one centralized place for monitoring.
Lp 77: Loyalty program
An initiative that provides customers incentives and rewards for frequent purchases or other behaviors to increase retention.
Fr 78: Framework
A basic conceptual structure and set of components used as a guide to build processes, strategies, and operations.
Ap 106: Advocacy program
A formal initiative focused on leveraging satisfied customers to actively promote products, services, or brands to new audiences.
Ob 107: Onboarding
The process of bringing new customers into effective use of a product or service through education, configuration, and support.
Op 108: Customer success operations
A role within a customer success team responsible for managing the systems and processes that help scale the delivery of services that drive adoption, renewal and expansion.
Dv 109: Data visualization
Presenting information and metrics visually through charts, graphs, and interactive reports for easier analysis.

Elements to define
Clearly defining foundational concepts ensures alignment across the organization. By providing consistent definitions and calculations for these metrics, CSMs can grade customer relationships and loyalty more accurately.
Some of the key elements in this category include:
Em 5: Engagement model
The structured approach and related strategies guide how a company interacts with and provides value to its customers.
Va 6: Value
The worth, utility, or benefits customers gain from a company's offerings and relationships in relation to cost, effort, and other alternatives.
Cq 7: Customer health quantifiers
Defined metrics and indicators used to monitor and measure the overall status and trajectory of customer relationships.
Mo 13: Monthly contract
A subscription billing and commitment period structure where customers pay monthly and can cancel anytime.
Sy 14: Storytelling
Crafting compelling narratives that connect customers to brands by meaningfully communicating user journeys, value, and human aspects.
Cx 15: Customer experience
The cumulative interactions and perceptions customers have with a company at all touchpoints along their relationship lifecycle.
Cb 31: Customer benefit
The positive outcomes and measurable value that customers gain from engaging with a product or service offering.
Sg 32: Customer success strategy
An overarching plan containing goals, initiatives, and processes focused on driving customer adoption, renewal and expansion.
Ue 48: User experience
The practical usability, enjoyment, and interactions customers have when leveraging a product or service.
Ht 49: High-touch engagement
Maintaining frequent, personalized and in-depth interactions with customers to build strong relationships and deliver maximum value.
Pe 50: Customer personas
Fictional representations of key customer segments synthesized from real data that capture demographics, behaviors, challenges, etc.
Cj 79: Customer journey
An examination of the full set of customer experiences and touchpoints from initial interest to the end of the relationship lifecycle.
Lt 80: Low-touch engagement
A hands-off engagement approach focused on efficient, digital self-service instead of personal account management.
Pc 81: Pricing
The enumerated costs charged to customers to purchase, license, access or subscribe to offerings.
Jo 110: Jobs-to-be-done
Focusing product design and messaging on fulfilling functional, emotional and social dimensions customers seek to resolve instead of surface features.
Pp 111: Customer pain points
Specific frustrating experiences, delays or challenges faced when trying to achieve goals that products can target.
Sl 112: Service level agreement
A standardized agreement documenting expectations, responsibilities and guarantees between a service provider and customer.

Ingredients for a powerful CSM
Certain qualities and resources are vital for CSMs to make an impact. When you add these qualities into the mix, CSMs have solid foundations to build better customer relationships. Without these “soft skills,” customer success would cease to exist as we know it.
We think the following elements are absolutely essential to ace a career in CS:
Cl 8: Collaboration
Working jointly with colleagues and partners both within and outside one's direct team to drive coordinated outcomes.
Tm 16: Time management
The practice of organizing tasks, priorities and schedules to increase efficiency, productivity and work-life balance.
Ep 33: Empathy
The ability to deeply understand and relate to another's emotions, experiences and motives to establish tighter bonds and trust.
Le 51: Leadership
Guiding, motivating and influencing colleagues and cross-functional partners towards achieving shared objectives.
Pr 82: Proactive
Acting in advance to anticipate possible customer issues and needs instead of waiting for customers to encounter problems.
Rb 113: Relationship building
Establishing rapport, trust and mutual understanding between people through open communication and shared experiences over time.

KPIs to track
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics for CSMs to monitor and gauge strategy effectiveness. Tracking KPIs and your progress not only identifies areas for improvement but also conveys value to stakeholders.
Key KPIs for customer success include:
Tv 2: Time-to-value
The length of time it takes customers to gain measurable business value and outcomes from a newly adopted product or service.
Lo 9: Customer loyalty
Customers' commitment to continue purchasing, promoting and referring a company's products and services over competitor options.
Ua 10: User adoption
The extent to which customers have actively embraced utilizing a product or service as an integral part of their workflows.
Re 17: Retention
Maintaining ongoing payment relationships with customers and preventing churn, turnover or cancellation.
Ar 18: Average revenue per user
The total revenue generated divided by the number of paying customers for a metric of individual customer monetization.
Ch 34: Churn
The percentage of customers that discontinue subscriptions or relationships with companies over a given timeframe.
Ip 35: Implementation
Executing the installation, configuration, migration, and training activities needed to successfully deploy a purchased product for access and use.
Ad 52: Advocacy
Turning customers into promoters that actively endorse, recommend and defend brands to drive referrals and growth.
Lc 53: Lifecycle stage
Where customers fall within the span of relationship phases from initial prospect to long-term retention targets.
Eg 53: Engagement
Interacting with customers by encouraging participation, collaboration, and providing resources relevant to their interests and needs.
Rg 84: Revenue generation
Developing pricing, sales processes and account expansion strategies focused on profitably monetizing customer relationships.
Ps 114: Product stickiness
Designing products, user journeys and post-purchase experiences that motivate habitual and consistent customer usage over time.
Ro 115: Return on investment
Comparing the financial return or payoff gained from an initiative relative to the resources and costs invested into it.

Means of research and communication
Communication and research provide crucial insights into customer needs and market trends. By researching and communicating effectively, CSMs can tailor strategies accordingly and help their customers achieve their desired outcomes quickly.
Key elements in this category include:
Ia 57: In-app messaging
Communicating directly with customers via messages within a mobile app or web application.
Au 58: Automation
Leveraging artificial intelligence technology to complete defined tasks and workflows without manual intervention to increase efficiency.
Pd 59: Product documents
Reference materials covering product capabilities, instructions, best practices and technical specifications.
Fe 60: Customer feedback
Direct input collected from users about their sentiments, ideas, and experiences regarding offerings.
Ci 61: Customer insights
Findings which reveal customer preferences, pain points, and behavior patterns derived from various data sources.
Ct 62: Customer relationship management
Tools and systems for managing all customer interactions and data to enhance engagement across lifecycles.
Da 62: Data analytics
Techniques used to assess and extract meaningful patterns, metrics and insights from large, complex data sets.
Vc 64: Voice of the customer
Represents the distinct needs, expectations, sentiments and concerns expressed directly by the customer.
Me 65: Metrics
Quantifiable measures used to set targets and gauge performance in achieving business objectives.
Ms 66: Messaging
Communication channels facilitating direct dialogues between companies and users or among customer communities.
Nf 67: New product feature
Recently introduced functionality or capabilities added to an existing product.
Ml 68: Machine learning
Software algorithms that can improve and adapt to new data without re-programming based on pattern inferences.
Sv 69: Survey
A standardized set of questions distributed to collect self-reported customer insights at scale.
Te 70: Testimonials
Positive recommendations from current customers endorsing a company and its offerings.
Rv 89: Reviews
Public customer opinions evaluating their first-hand experiences with products and services.
Tk 90: Ticketing system
A customer relationship management tool used to log, track, route and resolve issues or information requests reported by users.
St 91: Support tickets
Cases within a ticketing system documenting individual customer issues, questions or needs.

Key customer success ingredients
Without your core ingredients, you simply won’t have a customer success strategy. Period. These few fundamental entities are the reason customer success strategies work. They’re the DNA of it all – without it, you’ve got nada.
By 92: Buyer
The individual or group responsible for researching solutions, deciding on purchases and managing vendor relationships on behalf of an organization.
Cm 93: Customer Success Manager
A professional responsible for ensuring clients are satisfied with a company's products or services, fostering long-term relationships and aiding in their successful use and implementation.
Ct 94: Customer
Those who pay to access, use or benefit from a company's products and services.
Co 95: Chief Customer Officer
An executive-level role accountable for the end-to-end customer experience, satisfaction and lifecycle relationship management.
Us 96: User
The individual employees or customers actually leverage a purchased product or service within an organization.
Ou 97: Outcomes
The concrete business objectives, solutions and measurable results customers aim to achieve.
Su 98: Customer support
A team responsible for addressing user questions, troubleshooting issues, and resolving account problems.
Sa 99: SaaS
A software distribution model where applications are centrally hosted and accessed by customers via the internet.
Am 100: Account Manager
A post-sales professional responsible for a book of assigned customers and fostering individual account relationships, traditionally revenue-driven.
Vp 101: Vice President of Customer Success
An executive leading the company's retention, support and customer satisfaction strategies across the user lifecycle.
Dc 102: Director of Customer Success
A customer success leader managing a team of managers and front-line account representatives.
















 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn